Prodrug of phenytoin that converts to the anticonvulsant, phenytoin, after parenteral administration. Thought to modulate the sodium channels of neurons, calcium flux across neuronal membranes, and enhance the sodium–potassium ATPase activity of neurons and glial cells. The cellular mechanism of phenytoin is thought to be responsible for the anticonvulsant activity of fosphenytoin. Control of generalized convulsive status epilepticus and the prevention and treatment of seizures during neurosurgery, or as a parenteral short-term substitute for oral phenytoin.

FOSPHENYTOIN SODIUM
Structure
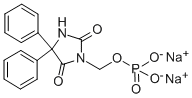
Product Description
Details |
|
|---|---|
Chemical Name |
FOSPHENYTOIN SODIUM |
IUPAC Name |
disodium [2,5-dioxo-4,4-di(phenyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]methyl phosphate |
CAS Number |
92134-98-0 |
Molecular Formula |
C16H13N2Na2O6P |
Synonyms |
CI 982;Cetebyx;ACC-9653;FOSPENYTOIN;ACC 9653-010;Pro-Epanutin;Fosphenytion SodiuM;FOSPHENYTOIN SODIUM;Fosphenytoin SodiuM USP;FOSPHENYTOIN DISODIUM SALT |
Application |
Anti epileptic |