Testosterone is a steroid sex hormone found in both men and women. In men, testosterone is produced primarily by the Leydig (interstitial) cells of the testes when stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH). It functions to stimulate spermatogenesis, promote physical and functional maturation of spermatozoa, maintain accessory organs of the male reproductive tract, support development of secondary sexual characteristics, stimulate growth and metabolism throughout the body and influence brain development by stimulating sexual behaviors and sexual drive. In women, testosterone is produced by the ovaries (25%), adrenals (25%) and via peripheral conversion from androstenedione (50%). Testerone in women functions to maintain libido and general wellbeing. Testosterone exerts a negative feedback mechanism on pituitary release of LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Testosterone may be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol depending on the tissue.

TESTOSTERONE
Structure
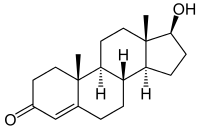
Product Description
Details |
|
|---|---|
Chemical Name |
TESTOSTERONE |
IUPAC Name |
(8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)- 17-Hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17- dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one |
CAS Number |
58-22-0 |
Molecular Formula |
C19H28O2 |
Synonyms |
17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; testosterone--dea schedule iii; testosterone standard solution; testosterone gamma-irradiated cell*culture tested; testosterone cell culture tested--dea*schedule ii; Testosterone,99%; 17-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; (17beta)-17-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; (8xi,9xi,14xi,17beta)-17-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one |
Application |
To be used as hormone replacement or substitution of diminished or absent endogenous testosterone. |