Omeprazole is a cell-permeable, selective proton pump inhibitor. Omeprazole undergoes an acid-catalyzed rearrangement to a thiol-reactive cationic sulfenamide that inhibits (H+-K+)-ATPase in the gastric milieu. Omeprazole also acts as an aryl hydrocarbon-like inducer of cytochrome P450 secretion in human liver. This compound is an inhibitor a variety of CYP isoenzymes, including CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP3A.

OMEPRAZOLE BASE
Structure
Product Description
Details |
|
|---|---|
Chemical Name |
OMEPRAZOLE BASE |
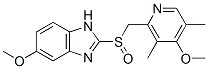
IUPAC Name |
6-methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole |
CAS Number |
73590-58-6 |
Molecular Formula |
C17H19N3O3S |
Synonyms |
miol;elgam;zimor;ANTRA;LOSEC;aulcer;prysma;ulcsep;MEPRAL;ZOLTUM |
Application |
A selective proton pump and CYP inhibitor |