Loperamide Hydrochloride is an opiate agonist with selectivity for the MOR (μ-opiod receptor). This specificity for μ-opioid receptors and limited penetrability into the brain prevent Loperamide from demonstrating central systemic effects generally associated with opiates, instead demonstrating localized action on the nociceptor and resultant antihyperalgesic action. Loperamide is shown to have an effect on the Ca2+ flux through high-voltage-activated calcium channels in response to high levels of extracellular K+, and at higher concentrations Loperamide is also a calcium channel protein inhibitor via the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-operated ion channel.

Loperamide Hcl
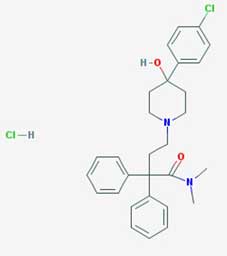
Structure
Product Description
Details |
|
|---|---|
Chemical Name |
Loperamide Hcl |
IUPAC Name |
4-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-N,N-dimethyl-2,2-di(phenyl)butanamide |
CAS Number |
34552-83-5 |
Molecular Formula |
C29H33CIN2O2.HCL |
Synonyms |
blox;pj185;imosec;r18553;Imosse;Clalet;imodium;lopemid;lopemin;loperyl |
Application |
Antidiarrheal |